info:Key Features
Cantilever walls
Anchored walls
Strutted excavations
Sheet pile walls
RC Diaphragm walls
Factor of Safety calculation in accordance with
Eurocode 7 and BS 8002
Bending moments and wall displacements calculated by finite
element analysis
Construction sequence and Berm excavation modelled
Soil arching and Soil-wall gap modelled
Non-linear elastic/plastic soil model
Hydrostatic or non-hydrostatic water pressures. Automatic water pressure balancing option
Uniform or variable surcharges applied at or below ground level
Structural loads applied to the wall
Fully automatic calculation of earth pressures
Simple data input with interactive Help
Hot Keys for instant Help, Error reporting, Data plot and
Summary output
Free choice of units
Graphical output of data and results
Fully documented
WALLAP is a powerful, fast and user-friendly program for analysing the
stability of cantilevered and propped retaining walls. WALLAP is
suitable for the analysis of both temporary works, such as sheet pile
walls, and permanent works such as reinforced concrete diaphragm walls
and contiguous bored pile walls.
Factors of safety are computed according to standard codes of practice
while wall displacements and bending moments are calculated by a finite
element analysis which models the actual sequence of construction of
the wall. Earth pressures are calculated automatically from basic soil
properties.
The strata profile consists of up to 40 soil types with hydrostatic or
non-linear water pressure distributions. Surcharges may be applied and
removed while struts and anchors may be installed and removed. The
program is menu driven with context sensitive Help and on-line access
to the comprehensive User Manual giving detailed guidance on data input
and interpretation of results.
Methods of Analysis
WALLAP offers two separate types of analysis within the one program:
Limit Equilibrium Analysis
Calculation of Factors of Safety according to one of the
following methods:
BS 8002 (Burland-Potts)
Eurocode 7 (Strength factor method)
British Standard Code of Practice No.2
BSC Piling Handbook
Bending moment and Displacement Analysis
Modelling of the stage by stage development of forces and wall
movements as construction proceeds. The wall and soil are modelled as a
beam and springs. Two spring models are available:
Subgrade reaction analysis (for routine design)
2-D Finite element analysis (for a more rigorous approach)
Modelling the Construction Sequence
The following types of construction activity may be specified and
combined in any order so as to model the construction sequence:
Excavate (including berms)
Fill
Change water pressures
Install and remove struts or anchors
Apply and remove surcharges
Apply loads to the wall
Apply rotational restraints to the wall
Change soil properties
Change wall stiffness
Soil Properties
A maximum of 40 different soil types can be defined including:
Cohesive / cohesionless
Drained / undrained
Normally / over-consolidated
Soil strength is defined in terms of Ka, Kac, Kp, Kpc and cohesion.
There is a Help facility to derive Ka etc.. from soil, wall friction
and backfill angles.
Soil stiffness is expressed in terms of Young's modulus and Poisson's ratio.
Optional soil properties include:
Linear variations of cohesion and modulus with depth.
Arching active behaviour
Simple non-linear elastic soil model
Struts and Anchors
Struts or anchors can be installed at up to 40 levels and may be pre-stressed. Struts can also be removed after installation.
Water Pressures
Hydrostatic or non-hydrostatic Water Pressure Profiles may be defined
on both sides of the wall, to model a variety of complex conditions
including:
Seepage
Submerged ground
Perched water tables
Uplift pressures under structures.
Automatic water pressure balancing option. This offers a convenient way
of balancing water pressures at the toe of the wall by assuming a
linear variation of piezometric head between the water levels either
side of the wall.
Surcharges
Surcharges can be applied at or below ground level on the active or
passive side of the wall. All surcharges are defined over a rectangular
loaded area. Ramp surcharges can be defined i.e. Surcharge magnitude
may vary linearly with distance from the wall.
Loads and Restraints
Horizontal and moment loads
may be applied to the wall. Rotational spring restraints may be applied
at any elevation in order to model the effect of floor slabs which are
built into the wall.
Data Input and Editing
Data entry is menu driven. Data values are checked for permissible
ranges. A list of data Errors and Warnings is displayed if unacceptable
or inappropriate data combinations are detected. Data can be checked
visually at any time during data entry or editing.
Units
Data may be entered in any consistent set of units e.g. (kN,m),
(lb,feet). All print-out from the program is automatically annotated in
the appropriate units.
Output from the Program
Output from the program consists of the following:
Listing of input data
Output at selected stages of:
- Factors of safety
- Bending moments and shear forces
- Wall pressures
- Displacements
- Strut/anchor forces
Summary output of:
- Factors of Safety at each stage
- Strut forces at each stage
- Maximum/minimum bending moment and displacement at each stage
- Cumulative bending moment and shear force envelopes
- Cumulative displacement envelope
Output to an Excel spreadsheet
- Tabulated results for selected stages can be sent to an .xls file
Graphics
Data and results are displayed in graphical form either on the screen or in hard copy. Graphical display of the data shows:
The soil profile,
Water pressure profiles,
Surcharges,
Applied loads/restraints,
Strut positions,
Boundary conditions.
Results are displayed in the form of:
Bending moment diagrams,
Shear force diagrams,
Wall pressure diagrams,
Wall displacement diagrams.
Hot Keys
Special Hot Keys give instant access to Help facilities, Error
reporting, Data plotting (during edit) and Summary output (during
analysis).
Help
Help is provided at two levels:- Press F1 at any time for context
sensitive help on data entry or current activity. Press Alt+H at any
time to use the Help Index. Subjects covered include advice on the
selection of values of earth pressure coefficients and soil modulus.
Hardware Requirements
WALLAP version 5 operates on all Windows systems. Program files occupy
about 1.5Mb of disk space. Operation of the program requires about 10Mb
off RAM.
screenshots: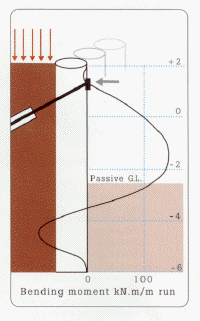 Download Links:
Download Links: 
